Scripts
Scripts allow you to define custom commands that can be executed as part of your workflow. They can be used to perform a variety of tasks, such as building your application, running database migrations, or sending notifications.
Scripts allow you to specify and execute custom logic. Defining scripts in your Stacktape configuration offers several benefits:
- They are easily reusable by all members of your team.
- They can be executed automatically as part of lifecycle hooks (e.g., before/after
deploy/delete) or manually using the `script:run` command. - You can use the
connectToproperty to easily inject environment variables for connecting to your stack's resources. - You can leverage bastion scripts and tunneling to access resources that are only available within a VPC.
There are three types of scripts:
local-script: Executed locally on the same machine where the Stacktape command is run.local-script-with-bastion-tunneling: Same aslocal-script, but connections to resources in theconnectTolist are tunneled through a bastion host, allowing you to access VPC-only resources.bastion-script: Executed on the bastion host itself.
Scripts can be either shell commands or files written in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python.
scripts:buildWeb:type: local-scriptproperties:executeCommand: npx gatsby buildhooks:beforeDeploy:- scriptName: buildWeb
Local script
A local script is executed on the same machine where the Stacktape command is run.
- The script must define one of the following properties:
executeCommand,executeScript,executeCommands, orexecuteScripts. - You can use the
connectToproperty to list the resources that your script needs to access. Stacktape will automatically inject the necessary environment variables for connecting to those resources. For more information, see Connecting to resources.
executeCommand
A single terminal command to execute in a separate shell process.
The command runs on the machine executing the Stacktape command. Be aware of potential differences between local and CI environments (e.g., OS, shell). You can only use one of executeScript, executeScripts, executeCommand, or executeCommands.
scripts:buildWeb:type: local-scriptproperties:executeCommand: npx gatsby build
executeScript
The path to a script file to execute. The script can be written in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python and runs in a separate process.
The executable is determined by defaults:configure or the system default (node for JS/TS, python for Python). You can only use one of executeScript, executeScripts, executeCommand, or executeCommands.
scripts:sendSlackNotification:type: local-scriptproperties:executeScript: scripts/send-slack-notification.ts
import { WebClient } from "@slack/web-api";const token = "my-access-token";const conversationId = "my-conversation-id";const slackClient = new WebClient(token);const errorData = JSON.parse(process.env.STP_ERROR);(async () => {await slackClient.chat.postMessage({channel: conversationId,text: errorData.message});})();
executeCommands
A list of terminal commands to execute sequentially. Each command runs in a separate shell process.
The commands run on the machine executing the Stacktape command. Be aware of potential differences between environments. You can only use one of executeScript, executeScripts, executeCommand, or executeCommands.
scripts:buildWeb:type: local-scriptproperties:executeCommands:- poetry run python manage.py makemigrations- poetry run python manage.py migrate
executeScripts
A list of script files to execute sequentially. Each script runs in a separate process.
The script can be written in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python. The executable is determined by defaults:configure or the system default. You can only use one of executeScript, executeScripts, executeCommand, or executeCommands.
scripts:sendSlackNotification:type: local-scriptproperties:executeScripts:- scripts/run-migration.ts- scripts/send-slack-notification.ts
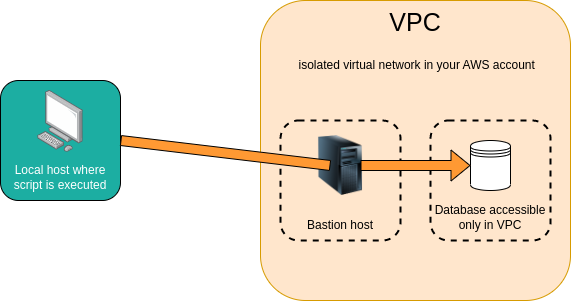
Local script with bastion tunneling
A local script with bastion tunneling is executed in the same way as a regular local script, but connections to the resources listed in the connectTo property are tunneled through a bastion server.
- This provides a secure, encrypted connection to your resources.
- It allows you to connect to resources that do not have a public endpoint and are only accessible within the stack's default VPC, such as a private
relational-databaseorredis-cluster. - The environment variables injected by the
connectToproperty are automatically adjusted to use the tunneled endpoints.
Your stack must have a bastion resource to use this type of script.
scripts:migrateDb:type: local-script-with-bastion-tunnelingproperties:executeScript: migrate.tsconnectTo:- myDatabasehooks:afterDeploy:- scriptName: migrateDbresources:myBastion:type: bastionmyDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:# database is only accessible from withing VPCaccessibility:accessibilityMode: vpcengine:type: postgresproperties:version: '16.2'primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t3.microcredentials:masterUserPassword: my_secret_pass
import { DbClient } from './db';// using environment variable which was automatically injected thanks to connectTo property// injected environment variables are using tunneled endpointconst databaseConnectionString = process.env.STP_MY_DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING;const client = new DbClient({ connectionString: databaseConnectionString });// perform migrations with the clientclient.close();
Bastion tunneling is supported for the following resource types:
relational-databaseredis-clusterapplication-load-balancerprivate-service(withloadBalancing.typeset toapplication-load-balancer)
Bastion script
A bastion script is executed remotely on a bastion server.
- Logs from the script's execution are streamed in real-time to your local machine.
- This provides a unified way to execute a set of commands from anywhere.
- You can use the
connectToproperty to list the resources that your script needs to access. Stacktape will automatically inject the necessary environment variables for connecting to those resources. For more information, see Connecting to resources.
scripts:dbScript:type: bastion-scriptproperties:executeCommands:- psql $STP_MY_DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING -c "SELECT 1 where 1=1"connectTo:- myDatabasehooks:afterDeploy:- scriptName: dbScriptresources:myBastion:type: bastionproperties:runCommandsAtLaunch:- yum update- yum install postgresql.x86_64 -ymyDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:accessibility:accessibilityMode: vpcengine:type: postgresproperties:version: '16.2'primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t3.microcredentials:masterUserPassword: my_secret_pass
Connecting to resources
A list of resources the script needs to interact with. Stacktape automatically injects environment variables with connection details for each specified resource.
Environment variable names are in the format STP_[RESOURCE_NAME]_[VARIABLE_NAME] (e.g., STP_MY_DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING).
Injected Variables by Resource Type:
Bucket:NAME,ARNDynamoDbTable:NAME,ARN,STREAM_ARNMongoDbAtlasCluster:CONNECTION_STRINGRelationalDatabase:CONNECTION_STRING,JDBC_CONNECTION_STRING,HOST,PORT. For Aurora clusters,READER_CONNECTION_STRING,READER_JDBC_CONNECTION_STRING, andREADER_HOSTare also included.RedisCluster:HOST,READER_HOST,PORTEventBus:ARNFunction:ARNBatchJob:JOB_DEFINITION_ARN,STATE_MACHINE_ARNUserAuthPool:ID,CLIENT_ID,ARNSnsTopic:ARN,NAMESqsQueue:ARN,NAME,URLUpstashKafkaTopic:TOPIC_NAME,TOPIC_ID,USERNAME,PASSWORD,TCP_ENDPOINT,REST_URLUpstashRedis:HOST,PORT,PASSWORD,REST_TOKEN,REST_URL,REDIS_URLPrivateService:ADDRESSWebService:URL
scripts:dbScript:type: local-scriptproperties:# The $STP_MY_DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING environment variable is injected by connectToexecuteCommands:- psql $STP_MY_DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING -c "SELECT * FROM users"connectTo:- myDatabaseresources:myDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:engine:type: postgresproperties:primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t3.micro
If you are using a local-script-with-bastion-tunneling script, connections to the resources listed in the connectTo property are tunneled through a bastion host. This allows you to access resources that are only accessible from within the VPC and increases the security of the connection. For more information, see Local script with bastion tunneling.
How to execute a script
A script can be executed in two ways:
-
Using the
script:runcommand:stacktape script:run --scriptName <<scriptName>> --stage <<stage>> -
Inside a hook.
Environment variables
A list of environment variables to pass to the script or command.
Values can be:
- A static string, number, or boolean.
- The result of a custom directive.
- A reference to another resource's parameter using the `$ResourceParam` directive.
- A value from a secret using the `$Secret` directive.
scripts:migrateDb:executeScript: scripts/migrate-db.tsenvironment:- name: DB_CONNECTION_STRINGvalue: $ResourceParam('mainDatabase', 'connectionString')resources:mainDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:credentials:masterUserPassword: my_secret_passwordengine:type: mysqlproperties:primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t2.micro
Permissions
You can use the assumeRoleOfResource property to grant a script the same AWS permissions as a specific resource.
The name of a deployed resource whose IAM role the script should assume. This grants the script the same permissions as the specified resource.
The resource must be deployed before the script is executed. Stacktape injects temporary AWS credentials as environment variables, which are automatically used by most AWS SDKs and CLIs.
Supported Resource Types:
functionbatch-jobworker-serviceweb-serviceprivate-servicemulti-container-workloadnextjs-web
scripts:seedDb:executeScript: scripts/seed-db.tsassumeRoleOfResource: myFunctionenvironment:- name: TABLE_NAMEvalue: $ResourceParam('dynamoTable', 'name')resources:dynamoTable:type: dynamo-db-tablemyFunction:type: functionproperties:allowAccessTo:- dynamoTable

