Redis Clusters
Redis is a fast, in-memory, NoSQL data store that provides sub-millisecond latency. It's often used as a cache to offload primary database systems, but it's also suitable for chat applications, message queues, and real-time analytics.
With Stacktape, you can deploy a fully managed Redis cluster without worrying about capacity scaling, hardware provisioning, cluster setup, patching, or backups. The service is compatible with open-source Redis, so you can use your existing Redis clients.
Under the hood, Stacktape uses Amazon ElastiCache for Redis.
When to use it
Redis is an excellent choice when performance is critical.
Advantages
- Performance: As an in-memory data store, Redis can deliver sub-millisecond response times, making it an order of magnitude faster than disk-based databases.
- Fully managed: Stacktape handles all the operational overhead, including scaling, provisioning, patching, and backups.
- High availability: Supports both clustered and non-clustered modes and provides automatic failover with minimal impact.
Disadvantages
- Data persistence: While Redis offers persistence options like snapshotting and append-only files, it's not as durable as a transactional database with full logging and point-in-time recovery.
- Memory limitations: All of your data must fit in memory.
- Client complexity: Clients connecting to a Redis cluster need to be aware of the cluster's topology, which can require additional configuration.
Basic usage
This example shows a simple, single-node Redis cluster. The only required properties are instanceSize and defaultUserPassword.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')myFunction:type: functionproperties:packaging:type: stacktape-lambda-buildpackproperties:entryfilePath: path/to/my/lambda.tsjoinDefaultVpc: trueconnectTo:- myRedisCluster
A Lambda function connected to a single-node Redis cluster.
import { Redis } from 'ioredis';const redisClient = new Redis(process.env.STP_MY_REDIS_CLUSTER_CONNECTION_STRING);const handler = async (event, context) => {await redisClient.set('currentTime', `${Date.now()}`);const value = await redisClient.get('currentTime');return { result: value };};export default handler;
Example code for storing and retrieving data from the cluster.
Instance size
This applies to both primary and replica nodes. Different instance sizes offer varying amounts of memory and network performance. You can change the instance size without interrupting the cluster or losing data.
For a detailed list of available instance types, see the AWS pricing page.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')
Default user password
Redis clusters are password-protected, and all communication is encrypted in transit. It is recommended to use secrets to manage this password instead of hardcoding it.
Password Constraints:
- Must contain only printable ASCII characters.
- Must be between 16 and 128 characters long.
- Cannot contain the following characters:
/,", or@.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')
Cluster topology
The topology of your cluster, determined by the number of replica nodes and shards, affects its performance and availability.
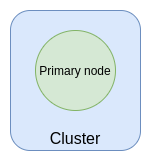
Single-node cluster
A single-node cluster has only one node and is not highly available.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')
Multi-node cluster
You can add replica nodes to a non-sharded cluster to improve read performance and availability.
Adding replica nodes (read replicas) provides two main benefits:
- Increased read throughput: Read requests are distributed across the replicas.
- Increased availability: If the primary node fails, a replica can be promoted to take its place.
Load balancing between replicas is handled automatically by AWS. For sharded clusters, this property specifies the number of replicas for each shard.
Note: You cannot change this value for a sharded cluster after it has been created.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')numReplicaNodes: 2

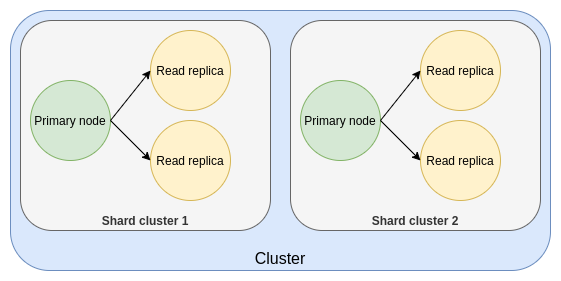
For horizontally scaled performance, you can enable sharding to distribute data across multiple primary nodes.
Sharding allows you to scale your Redis cluster horizontally by splitting the data across multiple shards. Each shard is managed by its own cluster, which includes a primary instance and a specified number of replicas. You can increase or decrease the number of shards without interrupting the cluster. Routing and re-balancing are handled automatically by AWS.
Limitations:
- Sharding can only be enabled when the cluster is first created.
- You cannot change the number of replica nodes (
numReplicaNodes) after a sharded cluster has been created. numReplicaNodesmust be at least1for sharded clusters.
For more details, see the AWS documentation.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')enableSharding: truenumShards: 2numReplicaNodes: 2
import { Cluster } from 'ioredis';const redisClusterClient = new Cluster([{host: process.env.REDIS_HOST,port: Number(process.env.REDIS_PORT)}],{redisOptions: { tls: {}, password: process.env.REDIS_PASSWORD },dnsLookup: (address, callback) => callback(null, address)});const handler = async (event, context) => {await redisClusterClient.set('currentTime', `${Date.now()}`);const value = await redisClusterClient.get('currentTime');return { result: value };};export default handler;
Using a sharded cluster from a Lambda function.
Logging
You can enable logging to send the Redis slow log to a CloudWatch log group.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')logging:format: json
Forwarding logs
You can forward logs to third-party services. See Forwarding Logs for more information.
Accessibility
You can configure which resources can access your cluster. Redis clusters don't support public IP addresses, so only two access modes are available.
VPC mode
The cluster is only accessible from resources within the default VPC. This includes any function, batch job, or container workload in your stack.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')accessibility:accessibilityMode: vpc
Scoped VPC mode
This mode is more restrictive. In addition to being in the same VPC, a resource must explicitly list the cluster in its connectTo property to gain access.
resources:myRedisCluster:type: redis-clusterproperties:instanceSize: cache.t3.microdefaultUserPassword: $Secret('redis.password')accessibility:accessibilityMode: scoping-workloads-in-vpc
Referenceable parameters
The following parameters can be easily referenced using $ResourceParam directive directive.
To learn more about referencing parameters, refer to referencing parameters.
In case of NON-sharded cluster(default), this is a hostname of the primary instance that can be used for both reads and writes. In case of sharded cluster, this is cluster's configuration endpoint that can be used for all operations.
- Usage:
$ResourceParam('<<resource-name>>', 'host')
Hostname (address) that can be used for reads only. (only available for NON-sharded clusters). If you use multiple replicas, it is advised to use readerHost for read operations to offload the primary host. ReaderHost automatically balances requests between available read replicas.
- Usage:
$ResourceParam('<<resource-name>>', 'readerHost')
Port of the cluster.
- Usage:
$ResourceParam('<<resource-name>>', 'port')
Indicates whether cluster is sharded. Available values:
enabledordisabled.- Usage:
$ResourceParam('<<resource-name>>', 'sharding')
Pricing
You are charged for:
- Nodes: The price depends on the instance size, number of shards, and number of replica nodes.
- Formula:
num_shards * (num_replica_nodes + 1) * price_per_node - Example 1 (cheapest): A single-node
cache.t3.microcluster costs $0.017/hour (~$12.50/month). - Example 2 (sharded): A two-shard
cache.t3.microcluster with one replica per shard costs $0.068/hour (~$49/month).
- Formula:
- Data transfer: Usually no additional cost.
- Backups: Free for the first day of retention, then $0.085/GB per month.
Free Tier (first 12 months)
- 750 hours of
t2.microort3.microinstances per month.
To learn more, see the AWS pricing page.

