Under the Hood
This guide explains what happens behind the scenes when you deploy a Stacktape application.
The Deployment Process
A Stacktape deployment consists of five phases:
-
Resolve & Validate Configuration: Stacktape compiles your
stacktape.ymlfile into a CloudFormation template. This template is a detailed blueprint of all the infrastructure resources required to run your application. -
Build & Package Code: Stacktape builds your application code and packages it into deployment artifacts, such as container images or Lambda function zip files.
-
Create Initial Resources: For a new stack, Stacktape creates an S3 bucket to store the deployment artifacts and a CloudFormation template, and an ECR repository to store container images. This step is skipped for subsequent deployments.
-
Upload Deployment Artifacts: Stacktape uploads the artifacts to the S3 bucket and ECR repository. To speed up this process, Stacktape uses caching and only uploads new or changed artifacts.
-
Deploy Infrastructure Resources: Stacktape uses the CloudFormation template to deploy your application and all its infrastructure resources. If an error occurs, the stack is automatically rolled back to the last working version.
Hot-Swap Deployments
For even faster deployments, Stacktape offers a hot-swap mode. If you've only changed your application code, Stacktape can bypass CloudFormation and update your Lambda functions and container resources directly. This can reduce deployment times from minutes to seconds.
Stack Resources
You can inspect all the resources in your deployed stack in the Stacktape console.
Naming Conventions
Stacktape uses a consistent naming convention for all your resources, which makes them easy to find in the AWS console.
For example, if you deploy a function named myLambda to the dev stage of a project named my-project, the Lambda function in AWS will be named my-project-dev-myLambda.
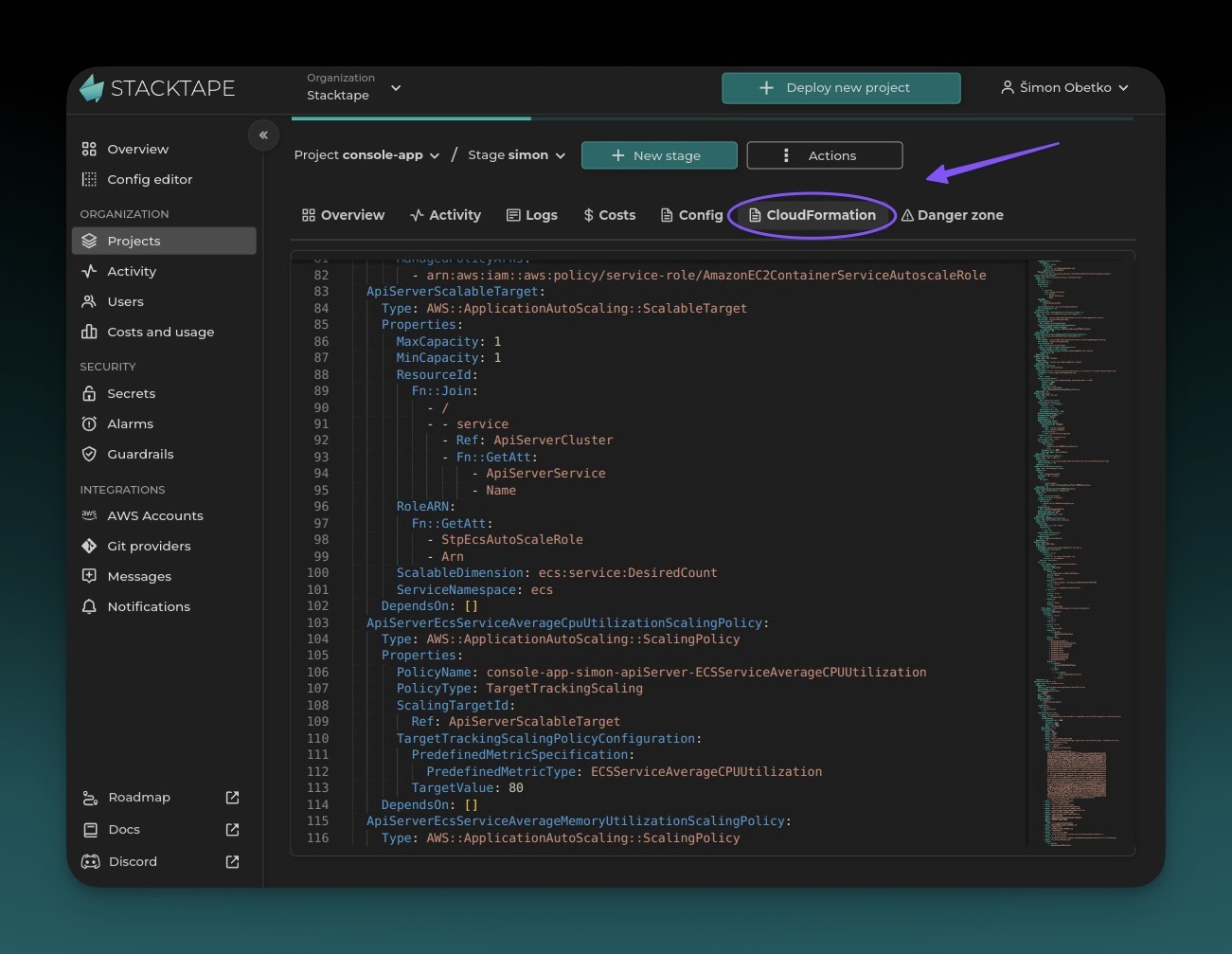
CloudFormation Template
You can view the complete CloudFormation template for your stack in the Stacktape console. This allows you to see exactly how your AWS resources are configured.
How Stacktape Extends AWS
Stacktape builds on top of AWS to provide a richer and more seamless developer experience.
Direct AWS API Calls
While CloudFormation is great for managing infrastructure, some tasks are outside its scope. Stacktape communicates directly with various AWS services to:
- Upload deployment artifacts.
- Monitor deployment progress.
- Perform hot-swap deployments.
- Detect the root cause of container failures.
- And much more.
Third-Party Resources
Stacktape allows you to provision resources from third-party providers like MongoDB Atlas and Upstash as if they were native AWS resources.
Stacktape manages these resources using open-source CloudFormation extensions, which are automatically installed and updated for you.

