CDNs
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to provide fast delivery of internet content. By caching content in locations closer to your users, a CDN can significantly reduce latency and decrease the load on your application's origin servers. It can also improve security by providing a layer of defense against DDoS attacks.
Under the hood, Stacktape uses Amazon CloudFront, which has over 300 points of presence (PoPs) worldwide.
How a CDN works
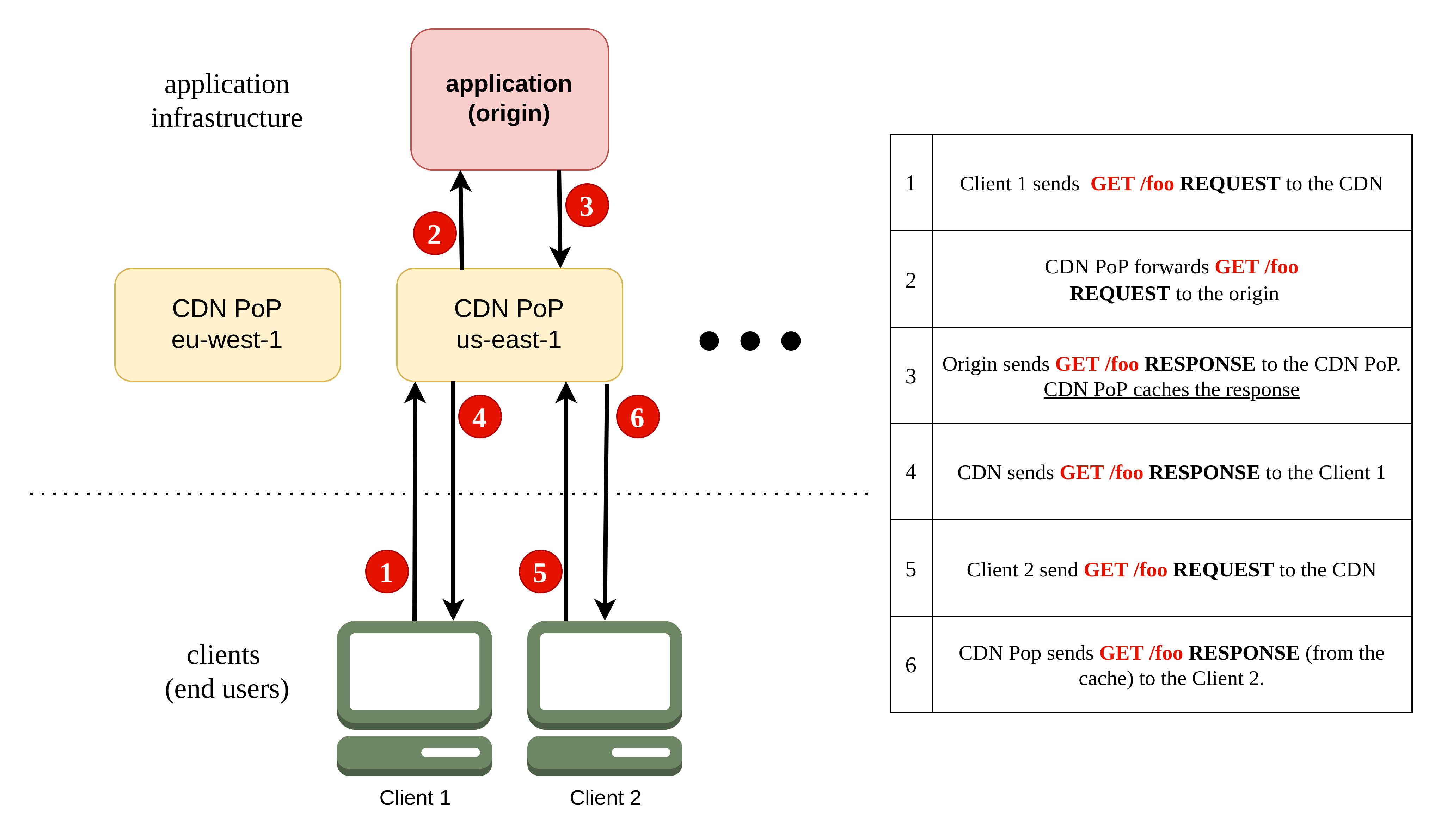
A CDN acts as a layer between your application (the origin) and your clients.
- Instead of sending requests directly to your application, clients send them to the CDN.
- The CDN routes the request to the nearest PoP.
- The PoP retrieves the response from your application (the origin).
- The PoP sends the response to the client and caches it for future requests.
- Subsequent requests for the same content can be served directly from the cache (a cache hit), which is much faster.
You can control which responses are cached and for how long. See the section on cache control for more information.
Basic usage
In Stacktape, you configure a CDN on a resource, which then becomes the default origin for the CDN. You can use a CDN with a bucket, HTTP API Gateway, or Application Load Balancer.
resources:myBucket:type: bucketproperties:cdn:enabled: true
You can also configure route rewrites to forward requests for specific paths to different origins. This allows you to create hybrid infrastructures where, for example, static content is served from a bucket and dynamic content is served from an API.
CDN with a bucket
You can enable a CDN for a bucket with just two lines of configuration. By default, content from the bucket is cached for six months. This is a common pattern for serving static websites.
resources:myBucket:type: bucketproperties:cdn:enabled: true
CDN with an HTTP API Gateway
You can also enable a CDN for an HTTP API Gateway. By default, the CDN does not cache any content from an API gateway, as it's assumed to be dynamic. You can control the caching behavior by setting the Cache-Control header in your API's responses.
resources:myApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: true
CDN with an Application Load Balancer
Similarly, you can enable a CDN for an Application Load Balancer. As with an API gateway, content is not cached by default.
resources:myLoadBalancer:type: application-load-balancerproperties:cdn:enabled: true
Custom domain names
When you connect a custom domain, Stacktape automatically:
- Creates DNS records: A DNS record is created to point your domain name to the resource.
- Adds TLS certificates: If the resource uses HTTPS, Stacktape issues and attaches a free, AWS-managed TLS certificate, handling TLS termination for you.
To manage a custom domain, it first needs to be added to your AWS account. This means that a hosted zone (collection of records managed together for a given domain) for your domain exists in your AWS account and your domain registrar's name servers are pointing to it. To learn more, refer to Adding a domain guide.
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: truecustomDomains:- domainName: mydomain.com
Edge Lambda functions
You can run Lambda functions at the edge to customize the content that the CDN delivers. For more information, see the Edge Lambda Functions page.
You can associate an edge-lambda-function with the CDN to be executed at different stages:
onRequest: Executed when the CDN receives a request from a client, before checking the cache.onResponse: Executed before returning a response to the client.
Potential Use Cases:
- Generating an immediate HTTP response without checking the cache or forwarding to the origin.
- Modifying the request (e.g., rewriting the URL or headers) before forwarding to the origin.
- Inspecting cookies or validating authorization headers and tokens.
resources:authFunction:type: edge-lambda-functionproperties:packaging:type: stacktape-lambda-buildpackproperties:entryfilePath: auth-function.tsmyBucket:type: bucketproperties:cdn:enabled: trueedgeFunctions:onRequest: authFunction
Cache control
You can control the caching behavior of the CDN in two ways:
- Using the
Cache-Controlheader (recommended): This gives you fine-grained control over the caching behavior for each response from your origin. - Using CDN caching options: This allows you to set basic caching rules but is less flexible.
Stacktape automatically invalidates the entire CDN cache after each successful deployment. This ensures that your users always receive the latest version of your content. You can disable this behavior in the automatic invalidation settings.
Cache-Control header with buckets
You can set the Cache-Control header for objects in a bucket using metadata. When you use the directory upload feature, Stacktape can automatically set the correct headers for you using presets.
resources:myBucket:type: bucketproperties:directoryUpload:directoryPath: my-web/buildheadersPreset: static-websitecdn:enabled: true
Cache-Control header with an HTTP API Gateway or Application Load Balancer
When using a CDN with an API gateway or an ALB, you can set the Cache-Control header in the responses from your application.
resources:myApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: truemyFunction:type: functionproperties:packaging:type: stacktape-lambda-buildpackproperties:entryfilePath: hello.tsevents:- type: http-api-gatewayproperties:httpApiGatewayName: myApiGatewaymethod: GETpath: /hello
export default async (event, context) => {return {statusCode: 200,statusDescription: '200 OK',isBase64Encoded: false,headers: {'Content-Type': 'text/plain','Cache-Control': 'max-age=30'},body: 'Hello !!!'};};
A Lambda function that returns a response with a Cache-Control header.
For more information on the Cache-Control header, see the MDN docs.
CDN caching options
You can specify default caching behavior for your CDN. Different caching options can be set for each route rewrite.
If you don't specify any caching options, Stacktape uses the following defaults:
| Origin type | minTTL | maxTTL | defaultTTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bucket | 0 | 31536000 | 15768000 |
| HTTP API Gateway | 0 | 31536000 | 0 |
| Application Load Balancer | 0 | 31536000 | 0 |
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: truecachingOptions:defaultTTL: 60routeRewrites:- path: /static/*cachingOptions:defaultTTL: 604800
Controlling the cache key
The cache key is a unique identifier for each object in the cache. It determines whether a request results in a cache hit. By default, the cache key is based on the URL path, but you can configure it to include headers, cookies, or query parameters.
If you don't specify a cache key, Stacktape uses the following defaults:
| Origin type | Parts of request included in cache key |
|---|---|
| Bucket | URL path |
| HTTP API Gateway | URL path, all query params, and the Authorization header |
| Application Load Balancer | URL path, all query params, and the Authorization header |
For example, if your origin uses the Accept-Language header to return different content based on the client's language, you should include that header in the cache key.
resources:myApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: truecachingOptions:cacheKeyParameters:headers:whitelist:- Accept-Language
CDN forwarding options
Forwarding options specify which parts of a request are forwarded to the origin. You can also filter which request methods are forwarded.
If you don't specify any forwarding options, Stacktape uses the following defaults:
| Origin type | Parts of request forwarded to origin |
|---|---|
| Bucket | URL path |
| HTTP API Gateway | URL path, all query params, all headers, and all cookies |
| Application Load Balancer | URL path, all query params, all headers, and all cookies |
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: trueforwardingOptions:allowedMethods:- 'GET'- 'POST'
Route rewrites
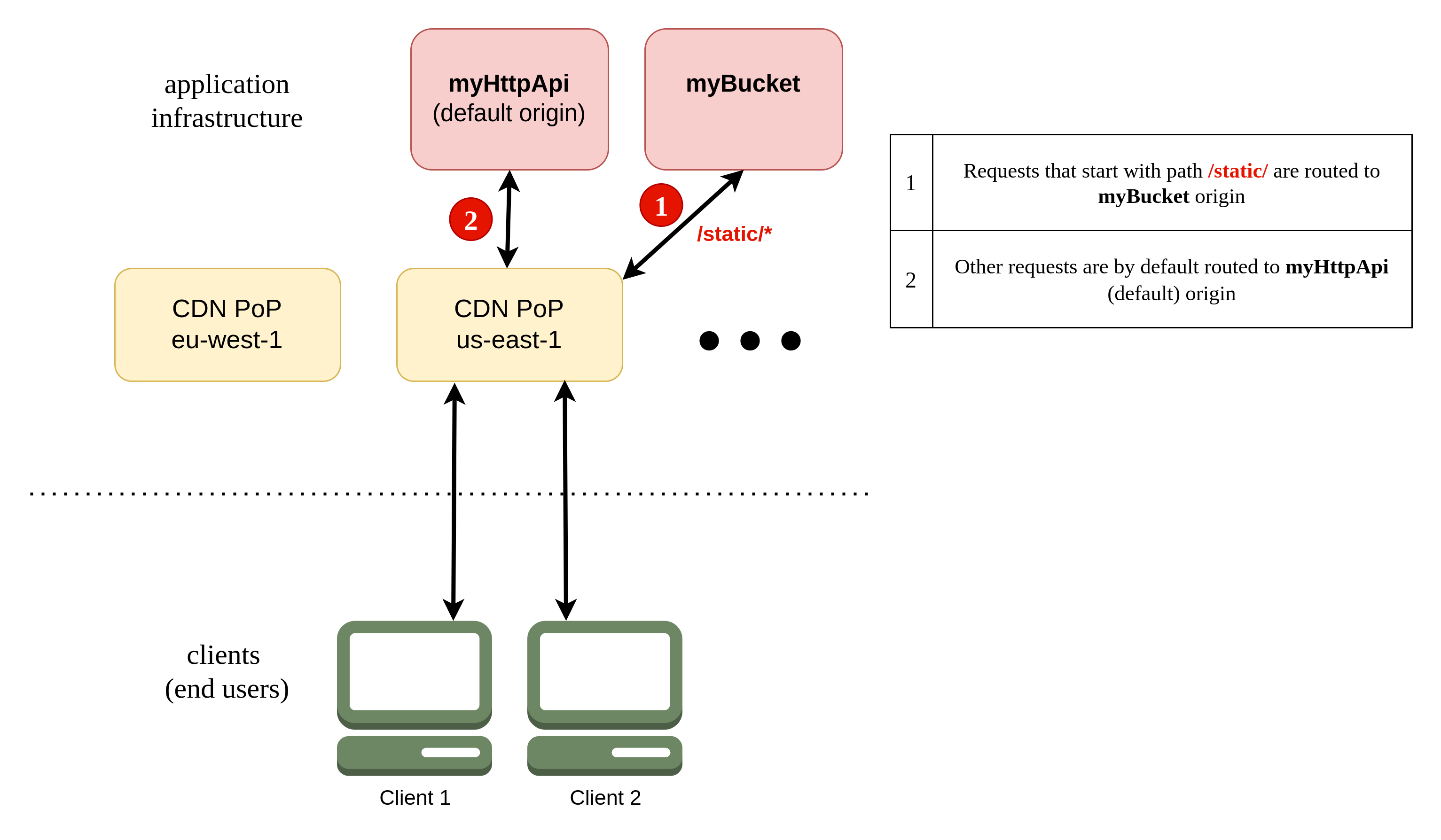
Route rewrites allow you to route incoming requests to different origins based on the URL path.
Each incoming request to the CDN is evaluated against a list of route rewrites. If the request path matches a rewrite's path pattern, it is sent to the configured route.
Route rewrites are evaluated in order, and the first match determines where the request will be sent. If no match is found, the request is sent to the default origin (the resource the CDN is attached to).
Example Use Cases:
- Serving static content from a bucket while routing dynamic paths to a Lambda function.
- Caching
.jpgfiles for a longer duration than other file types.
Routing to a bucket
In this example, requests with a URL path starting with /static are routed to a bucket, while all other requests are routed to an HTTP API Gateway.
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: truerouteRewrites:- path: /static/*routeTo:type: bucketproperties:bucketName: myBucketdisableUrlNormalization: truemyBucket:type: 'bucket'
Routing to an Application Load Balancer
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: truerouteRewrites:- path: /app2/*routeTo:type: 'application-load-balancer'properties:loadBalancerName: myLoadBalancermyLoadBalancer:type: 'application-load-balancer'
Routing to an HTTP API Gateway
resources:myHttpApi:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:cdn:enabled: truerouteRewrites:- path: /app2/*routeTo:type: 'http-api-gateway'properties:httpApiGatewayName: appApiGatewayappApiGateway:type: 'http-api-gateway'
Routing to a custom origin
resources:myLoadBalancer:type: 'application-load-balancer'properties:cdn:enabled: truerouteRewrites:- path: /external/*routeTo:type: custom-originproperties:domainName: my-custom-origin.example.com
Automatic invalidation
You can disable the automatic cache invalidation that occurs after each deployment by setting invalidateAfterDeploy to false.
resources:myApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: trueinvalidateAfterDeploy: false
Price class
You can set a price class to reduce the cost of your CDN by limiting the number of edge locations from which it serves traffic.
A higher price class results in more edge locations serving your traffic, which can improve performance in some regions but is more costly.
For example, if your users are primarily located in the US and Europe, you can save money by using PriceClass_100.
For more details, see the AWS documentation on price classes.
resources:myApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: truecloudfrontPriceClass: PriceClass_200
Firewall
You can protect your CDN with a web application firewall.
A web-app-firewall can protect your resources from common web exploits that could affect availability, compromise security, or consume excessive resources.
The firewall works by filtering malicious requests before they reach your application.
For more information, see the firewall documentation.
To learn more, see the Web Application Firewall documentation.
resources:myFirewall:type: web-app-firewallproperties:scope: cdnmyApiGateway:type: http-api-gatewayproperties:cdn:enabled: trueuseFirewall: myFirewall

