Bastion Servers (Jump Hosts)
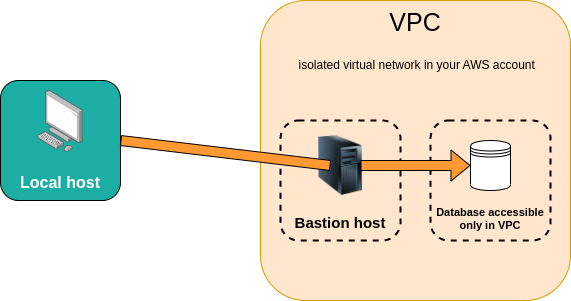
A bastion server, or jump host, is a virtual machine that provides secure access to resources that are isolated within a private network (VPC). This is useful for managing resources like databases or Redis clusters that don't have a public endpoint.
Connections to the bastion server are established using SSM Session Manager, which leverages your IAM permissions for authentication. This eliminates the need to expose any ports, providing a highly secure way to access your private resources.
Basic usage
resources:myBastion:type: bastion
Example of a bastion server configuration.
Connecting to a bastion server
You can start an interactive shell session on a bastion server using the bastion:session command:
stacktape bastion:session --stage <<stage>> --region <<region>> --bastionResource <<bastionResourceName>>
Creating a bastion tunnel
For resources that don't have a public endpoint, like a database, you can use a bastion tunnel to access them from your local machine. The bastion:tunnel command creates a secure pathway from a port on your local machine to the port of the target resource, using the bastion server as an intermediary.
stacktape bastion:tunnel --stage <<stage>> --region <<region>> --bastionResource <<bastionResourceName>> --resourceName <<nameOfTargetResource>>
Once the tunnel is established, Stacktape will print the local endpoint that you can use to connect to the resource.
Tunnel example
resources:myBastion:type: bastionmyDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:# database is only accessible from withing VPCaccessibility:accessibilityMode: vpcengine:type: postgresproperties:version: '16.2'primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t3.microcredentials:masterUserPassword: my_secret_pass
A bastion server with a database that is only accessible within the VPC.
To create a tunnel to the database, you would run:
stacktape bastion:tunnel --stage <<stage>> --bastionResource myBastion --resourceName myDatabase

Bastion tunneling is supported for the following resource types:
relational-databaseredis-clusterapplication-load-balancerprivate-service(when using an application load balancer)
Using a bastion with scripts
You can also use bastion servers with scripts. For more information, see the documentation on bastion scripts and local scripts with bastion tunneling.
scripts:migrateDb:type: local-script-with-bastion-tunnelingproperties:executeScript: migrate.tsconnectTo:- myDatabasehooks:afterDeploy:- scriptName: migrateDbresources:myBastion:type: bastionmyDatabase:type: relational-databaseproperties:# database is only accessible from withing VPCaccessibility:accessibilityMode: vpcengine:type: postgresproperties:version: '16.2'primaryInstance:instanceSize: db.t3.microcredentials:masterUserPassword: my_secret_pass
A Stacktape configuration that uses a bastion tunnel for a migration script.
Instance size
By default, bastion servers use a t3.micro instance, which is eligible for the AWS Free Tier. You can specify a different instance size using the instanceSize property. For a full list of available instance types, see the AWS documentation.
resources:myBastion:type: bastionproperties:instanceSize: c5.large
Custom commands on launch
You can run a custom set of commands when the bastion server is launched using the runCommandsAtLaunch property. This is useful for installing dependencies or performing other setup tasks.
- Commands are run as the
rootuser (do not usesudo). - Modifying this list after the bastion host has been created will force a replacement of the instance, meaning any manually created data on the old instance will be lost.
- Use this to install dependencies and packages that may be required for your bastion scripts.
resources:myBastion:type: bastionproperties:runCommandsAtLaunch:- yum update- yum install postgresql.x86_64 -y
All bastion hosts use the latest Amazon Linux 2023 operating system.
SSM sessions
Stacktape uses SSM Session Manager to provide secure access to bastion servers. This eliminates the need to manage SSH keys or open additional network ports, making it more secure than traditional SSH access.
Pricing
The price of a bastion server depends on its instance size. The default t3.micro instance is free for the first 12 months as part of the AWS Free Tier. After that, it costs approximately $7.50 per month.

